| Plant parts and main functions

ARBORICULTURE IS THE SCIENCE THAT ANALYSES HOW TO KNOW AND TREAT PLANTS
Nowadays in ornamental arboriculture, tree climbing is the most widely used working technique..



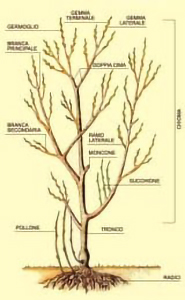
I would like to start by saying that trees are “autotrophic”: they are able to feed themselves by using solar power organic substances from the soil. A plants’ body is composed by different organs with certain functions. Mostly we will talk about conservative organs, which keep the plant alive and help it grow. Roots lie underground; they feed and anchor the tree to the ground. They can be divided into support and absorbents roots. The support ones have an anchor function, whose dimensions change according to the soil where they are planted. Absorbent roots, on the other hand, suck the sap from the soil and grow to the extremities of the woody roots: they are the so-called root hairs and are generally found at a depth of thirty to forty centimeters. These roots will expand according to tree and soil size; they often live in symbiosis with fungi. These are the mycorrhizae that, thanks to this combination, enable the right exchange of water and sugars.
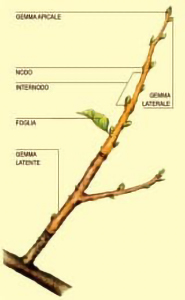
The greatest damage for trees are man-made injuries (caused by excavations, paving, soil compaction, etc) in the vicinity of the root system which usually involves an irreversible deterioration for the tree itself. The stem supports the plant and raises the foliage above the ground. It moves nutrients to branches, leaves, flowers and fruits. The branches (primary branches, secondary branches and twigs), which make up the foliage, grow progressively from the stem. The buds are divided in apical buds if they are on top of a stem or a branch; side buds when they are at the axil of a leaf or a twig; leaf buds when they produce an axis of single leaves; floriferous buds if they grow only flowers; mixed if they produce both leaves and flowers; ready buds are those that are able to vegetate; and finally dormant buds are those that will develop in the following season from their formation. Leaves are very important for plants: they are vital for the nutritional functions, together with roots and the stem, so they are considered the lungs of plants.
The leaves are distinguished by their duration in caducous or evergreen. Fallen leaf plants are those that are stripped of their leaves; evergreen those plants that hold it for several years, never being without them.



Once you have chosen the right and healthy plant and the place where you intend to put it, you can start with the plantation process. You will need an optimal habitat in order to start the planting process: land suitable for the plant; light exposure; good drainage, and non-constipated soil. Also important is the size of the hole, which must never be smaller than the size of the foliage. Therefore, seasons such as autumn and spring should be chosen, so as to avoid extreme cold or heat.
Be careful of the planting depth too; a too-deep planting can cause stress to the plant. Note that the ground must be at the same level of the collar (which is the area between the stem and the roots). Every tree needs water for the rooting phase. You must also prevent water from stagnating in the planting hole; indeed, it could rot the entire root system.
Talking about the planting place, we will need to take into account the future needs of the plant. We will need to pay attention to the volume of soil needed. Every single plant must have sufficient space available for its own unique needs, to avoid drastic pruning or demolition in the future.
The plant training is essential to grow the plant straight and it must always be done. It must be well anchored to the ground and it can’t be higher than a third of the entire plant. If the plant is small, training may not be necessary. Today we can make training systems with poles or innovate plot anchoring systems; that will avoid continuous care to the plant.
Upon regular request and authorisation, our company handles plants felling too, both in private and public gardens. With regards to tree felling, specific conditions, such as absence of damage to public or private buildings and public safety, are needed.











There are different reasons for pruning:






Menichelli provides a service to eliminate tree stumps, with rapid interventions throughout the country.
Stumps are an easily visible obstacle, but above all they represent a serious phytosanitary problem for trees and shrubs bordering the stump. indeed, stumps are quickly attacked by fungi; they spread and attack healthy plants roots up to 40 meters from the same stump. Menichelli di Calenzano, Florence therefore offers a stumps milling service with drills of various power and reduced weight. They are capable of crumbling large size stumps up to 60 centimeters deep, without damaging the surrounding soil, as it would happened through the use of excavators or tractors.
The service offered by Menichelli thanks to the cutter stumps is therefore: